How To Put Drive Band On Double Drive Wheel
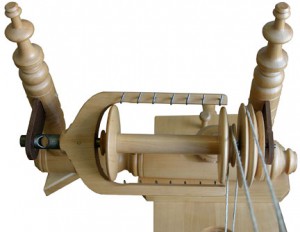 In-Depth Description of Double Drive Wheels
In-Depth Description of Double Drive Wheels
In that location was a fourth dimension when spinning wheels did not take bobbins and flyers. Yarn was spun on a bike that had just a spindle. While groovy yarn can be made in this style, it was a irksome procedure. Spinners had to do a long type of draw with the bicycle rotating ane management, then wind the yarn on the spindle by reversing the cycle direction. Start. Stop. Start. Stop. A better idea was waiting to be discovered.
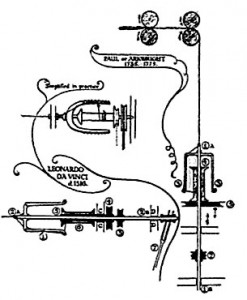
Leonardo da Vinci gave some thought to the efficiency of spinning, and it may have only taken a short time for him to visualize a mechanical method for assuasive a continuous process of spinning yarn without stopping and allow the ability to store the yarn equally production continued. It was all in his mind; however, he never really made the devise. Rather, he drew a remarkable sketch which fortunately survived him. The production of the get-go double drive flyer can exist attributed to Johann Jurgen of Federal republic of germany.
 There is virtually no difference in the bones design of this flyer from 1 wheel maker to the next. In about common practice, a unmarried drive band long enough to loop effectually the various mechanical parts twice is the drive transmission device. Think of information technology doing the same thing that the drive chugalug on a automobile motor does. Using the free energy source of a leg or two, the bulldoze bike is fabricated to rotate. The speed of this rotation volition affect the driven parts on the mother-of-all. The faster one treadles and the bore of the bulldoze wheel is one manner to control the speed of the driven parts of the spinning bike, the flyer and bobbin. The bulldoze band is the intermediate part that transfers power from the drive wheel to the flyer.
There is virtually no difference in the bones design of this flyer from 1 wheel maker to the next. In about common practice, a unmarried drive band long enough to loop effectually the various mechanical parts twice is the drive transmission device. Think of information technology doing the same thing that the drive chugalug on a automobile motor does. Using the free energy source of a leg or two, the bulldoze bike is fabricated to rotate. The speed of this rotation volition affect the driven parts on the mother-of-all. The faster one treadles and the bore of the bulldoze wheel is one manner to control the speed of the driven parts of the spinning bike, the flyer and bobbin. The bulldoze band is the intermediate part that transfers power from the drive wheel to the flyer.
But what happens at the flyer? How does the rotation of the flyer and bobbin result in the fibers turning into yarn and being drawn onto the bobbin?
The critical ingredients to this procedure are the diameter of the whorl (a pulley) and the pulley on the finish of the bobbin, coupled with the design/shape of the grooves on the scroll and bobbin pulley.
The groove(s) on the gyre take a very singled-out "5" shape to them, allowing the bulldoze band to sit at the very bottom and grip the sides of the groove. This gripping is what allows the flyer to exist rotated as the bulldoze bike turns. There should not be any slipping of the band in the ringlet groove merely tension on the drive band should exist no more than needed for the drive bike to rotate the flyer.
Now look at the groove on the bobbin caster. Properly made, this groove has a "U" shape to it. Dissimilar the whorl groove, the shape here on the bobbin pulley is designed to allow a sure amount of slipping of the bulldoze ring as information technology goes around the bobbin.
Both the whorl and the bobbin are "driven" past the drive ring, hence the term "double drive."
Here, in a list format, is what happens when a double bulldoze wheel is set up properly:
Pes or feet actuate the treadle(s);
Treadle movement causes footman to rise and autumn;
Footman pulls/pushes the crank on the drive wheel axle causing the wheel to rotate;
The drive bicycle rotation volition crusade the drive band, if tensioned properly, to travel around the circumference of the bike;
The moving bulldoze band will cause the flyer mechanism to rotate if properly tensioned;
The bulldoze band interacts with both the whorl and the bobbin caster independently, causing both to rotate if properly tensioned; these 2 parts can and volition rotate independently of one another; different revolutions per minute (rpm);
When yarn is secured to the bobbin core and routed through the flyer orifice and held securely in a spinner's hands, the flyer and the bobbin will rotate in sync, locked together by the yarn between bobbin and flyer; the drive band on the bobbin pulley is really slipping because of the "U" shape;
When the spinner allows twisted yarn to accelerate into the orifice a caste of tension is released on the yarn assuasive the lock of the bobbin and flyer to break; the bobbin will begin to rotate faster (considering the bobbin pulley is smaller in diameter) and information technology is at this time that yarn, pulled by the bobbin, comes through the orifice and onto the bobbin.
This all happens rather chop-chop and is difficult to run into, but the continuous process of the above steps volition result in yarn being made and loaded onto the bobbin.
Tension of the drive band impacts two aspects of spinning. First, the rotation of the flyer; second, the force of the take-upwardly of yarn onto the bobbin. In trying to arrange 1, you as well alter the other. Proper tension is thus a remainder of these two settings. A general rule is this: with the wheel at rest, you want to exist able to pull yarn off the bobbin through the orifice without the wheel turning. Your terminal tension may be more or less, depending on other factors. Inappropriate drive band tension is detrimental to the feel of treadling and is to exist avoided.
Hither are some other of import aspects of this design:
The rotation speed of the flyer can be adjusted past placing the drive band on a different diameter whorl groove or by treadle cadence;
The diameter of the bobbin pulley, in human relationship to the whorl diameter, is critical; as a rule, the bobbin pulley should exist a minimum of a third smaller than the diameter of the groove on the whorl for take-up to function. If your bobbin has a pulley on each end, have care that you exercise not use larger caster with a pocket-sized whorl;
The rotation speed of the flyer impacts how quickly twist is developed in the fibers in the spinner'southward manus.
With a double bulldoze wheel a hybrid option is possible which some spinners might desire to effort as it peradventure makes tensioning easier to empathize and set. Just use an elastic bulldoze band to bulldoze the flyer and a carve up cord ring to drive the bobbin and control have up.
Here is how it is done:
For the cord band, brand the length but so it will fit around the bike and the larger bobbin pulley when the "elevation" of the flyer is nigh its lowest setting. This volition let you to move the female parent-of-al to accommodate for the proper take upward or when y'all move the mother-of-all to employ the smaller caster on the bobbin with the smaller scroll. For the elastic ring, brand the length simply long enough to go around the smaller groove on the larger whorl in your set of two whorls. The elastic ring should non be over tensioned; but tight enough to take the flyer rotate without slipping when the drive bike turns. An elastic band that has a soft, rubbery surface that grips the whorl aggressively is a practiced affair.
Now you practice not demand to be overly concerned with the rubberband band; it adapts itself to the tension yous now set for the string band and take upwardly. Some adjustment to the length of the two bands may exist needed as y'all implement this method, but one time properly determined, any adjustment of the string tension to fine tune have up will allow the elastic band to adapt automatically.
How To Put Drive Band On Double Drive Wheel,
Source: https://kromskina.com/double-drive-description/
Posted by: purcellbrinelition.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How To Put Drive Band On Double Drive Wheel"
Post a Comment